A newer version of this article is available !
In a 3D application, implementing camera control is an essential step to provide interactive and intuitive content.
In this post, we will study a class that allows to easily control the camera : OrbitControls.

The OrbitControls class
The OrbitControls control class allows to make the camera orbit around a target. To use this class, we need to import it from the Three.js add-ons :
import { OrbitControls } from 'https://threejs.org/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js'
Then we create an OrbitControls instance in our code :
controls = new OrbitControls( camera, renderer.domElement );
Its constructor accepts two parameters : Our camera and the rendering engine of our application.
OrbitControls properties
This class provides us with several properties that allow us to adjust its behavior according to our needs ! In this chapter we will study three of them :
enableDampingdampingFactormaxpolarAngle
controls.enableDamping = true; controls.dampingFactor = 0.05; controls.maxPolarAngle = Math.PI / 2;
The enableDamping property
This class property is used to activate inertia : A progressive slowing down of the camera movement.
The value of this property must be set to true to activate the inertia. In this case, it is necessary to call the update() method of OrbitControls in the main loop.
function animate()
{
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
controls.update(); // controls.enableDamping = true
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
The dampingFactor property
This class property represents the coefficient of inertia of the camera.
La propriété maxPolarAngle
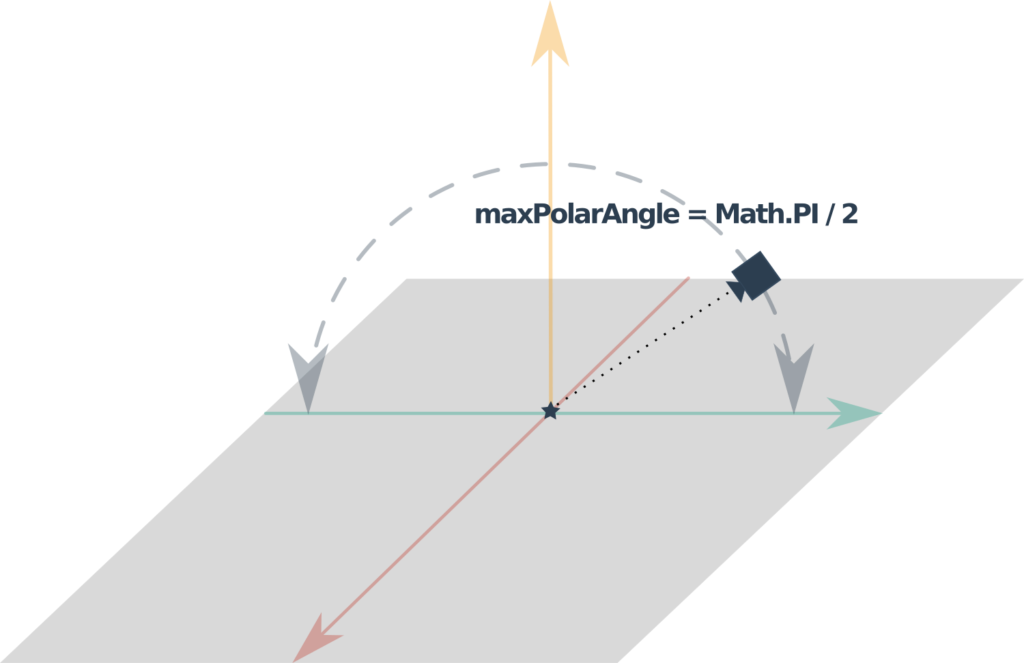
It is possible to define a maximum inclination of the camera through the maxPolarAngle property.
In our example, we want the maximum angle of the camera to be Math.PI / 2.
Final Result
See the Pen Orbit Controls by Thomas (@thomassifferlen) on CodePen.


[…] 20 juin 202125 août 2021 thomassifferlen 2 commentaires Available in English […]